Data Management
“The beginning of wisdom is the definition of terms.”
“The beginning of wisdom is the definition of terms.”
This is an old revision of the document!
A data issue is a non-fulfilment of a requirement regarding data quality.
Generally, a data issue concerns an incorrect data value, but it can be applied to any other data quality dimensions, e.g., completeness and timeliness.
Attributes of a data issue are:
| Phase | Activity | |
|---|---|---|
| Plan | * To detect or identify data issues * To determine if similar data issues exist * To register data issues * To count the number of data issues * To categorize or classify data issues * To diagnose data issues (‘root cause analysis’) * To formulate options for remediation of data issues. * To assess the business impact of data issues (‘severity’) * To prioritize data issues based on business impact (by data owners and data stewards) * To eventually escalate data issues. See figure. | |
| Do | * To eliminate or resolve a data issue (‘correction’, ‘remediation’, ‘scrubbing’ or ‘cleansing’) * To eliminate the cause of a data issue to prevent recurring (‘corrective action’) * To eliminate the cause of a potential data issue (‘preventive action’) * To deal with the consequences of the data issue, e.g., to report data issues to data consumers * To document actions taken. | |
| Check | * To monitor the status of data issues and their resolutions. * To review the effectiveness of corrective and preventive action. | |
| Act | * To adapt corrective and preventive action. |
| Characteristic | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Severity | Data issues are resolved in order of severity. |
The figure shows a possible escalation path of data issues.
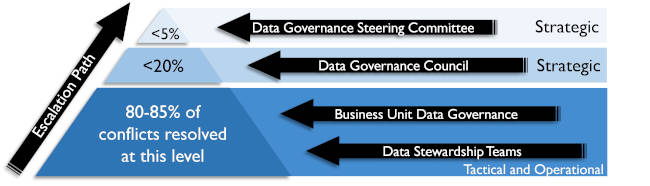 Figure 2: Data issue escalation path.
Figure 2: Data issue escalation path.
A customer of the TradeAll trade company complained that he had been delivered an incorrect item. The sales department reported this incident in the Incident Tracking System, which was assigned to the Data Steward. The Data Steward then went to see how this could have happened. He found that the item number did not match the item description and suspected that this was due to a data entry error. Based on the item number, the products were taken from the warehouse.
He corrected the item number (Correction), but to prevent this kind of error, he took the measure that the entry of items was checked by a second person to prevent more incidents (Corrective Action). He also made sure to check for duplicate item numbers in the database (Corrective Action).. The customer was apologised for the error and the correct article was delivered as soon as possible.
DAMA (2017). DAMA-DMBOK. Data Management Body of Knowledge. 2nd Edition. Technics Publications Llc. August 2017. Chapter 13 Data Quality, section 2.7.3 Develop Operational Procedures for Managing Data Issues.
DAMA Dictionary of Data Management. 2nd Edition 2011. Technics Publications, LLC, New Jersey.
ISO 9000:2015. Quality Management Systems – Requirements.
ISO 9001:2015. Quality Management Systems – Fundamentals and vocabulary.